Treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AMC) is excessive bleeding in duration (more than 8 days), volume of blood loss (more than 80 ml), frequency (less than 24 days or more than 38 days) and/or regularity (cycle variability >9 days).
Abnormal uterine bleeding can occur at any age, but is more common in women of reproductive and perimenopausal age. The main causes include fibroids, polyps, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia, and cancer.
Treatment of AMC depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In cases where drug therapy is not effective enough or there is a threat to life due to massive blood loss, surgical treatment is used. It is aimed at stopping bleeding and eliminating the causes of its occurrence, such as polyps or myomatous nodes.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs Blood test Endometrial biopsy Upon admission to the hospital, the following are required: Fluorography or chest X-ray Electrocardiography Laboratory examinations: general blood test, biochemical blood test, coagulogram, blood tests for hepatitis B and C, syphilis, HIV, smear for purity and smear for oncocytology from the cervix Determination of blood type and Rh factor
Surgical treatment begins with diagnostic hysteroscopy, which allows you to visualize the uterine cavity and identify pathological changes. Depending on the detected pathology, the doctor may perform one of the following interventions: Hysteroresectoscopy is a method in which pathological formations in the uterus are removed under the control of a hysteroscope. Curettage of the uterine cavity is a procedure in which the surface layer of the endometrium is removed to stop bleeding. Endometrial ablation is a radical method aimed at the complete destruction of the uterine mucosa, which leads to the cessation of menstruation. This method is used in perimenopausal or postmenopausal women who are not planning pregnancy.
Hysteroscope with a camera for imaging the uterine cavity Resectoscope for the removal of pathological formations Coagulation devices for stopping bleeding and endometrial ablation
After surgery, patients are advised to refrain from sexual intercourse and the use of tampons for 1-2 weeks. Minor spotting may occur for several days after surgery. To prevent recurrence of AMC and monitor the condition of the endometrium, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is surgical treatment necessary for uterine bleeding?
Can I get pregnant after surgical treatment of AMC?
Didn't find an answer to your question?
You can describe your problem in detail and ask a question to the doctor. He will answer you and help you find a solution
Specialists
Find a SpecialistSimilar referral activities
Removal of tumors in the intimate area
A procedure aimed at eliminating benign growths such as papillomas, warts, cysts and genital warts.
Reproductive surgery
Surgical treatment and simultaneous accurate diagnosis of female infertility factors: adhesions, endometriosis, congenital malformations of the genital organs, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, intrauterine pathology (septum and synechia), polycystic ovary syndrome.
Colposcopy procedure
A procedure in which a doctor can use a colposcope to examine the vagina, cervix and vulva, examine the mucous membrane in detail and identify abnormal changes that may be a sign of diseases.
Cervical plastic surgery
Cervical plastic surgery (tracheloplasty) is a surgical restoration of the anatomical structure and function of the cervix, which helps to maintain the health of the reproductive system.
Treatment of vulvar diseases
Vulvar diseases, including chronic fissures, sclerotrophic lichen and other dermatological conditions. We offer modern and effective treatment methods aimed at reducing symptoms and restoring the normal condition of the vulva skin.
Correction of menopause problems
The onset of menopause is often accompanied by a number of physical and mental manifestations unpleasant for a woman. The gynecologist will choose therapy, which can relieve or completely eliminate the symptoms.
News & Media
All news and mediaThe III All-Russian Progress Conference "Aesthetic Gynecology and Perineology: balance of beauty and functionality" was held in Moscow
The event lasted from 24 to 26 May, and the theme was Aesthetic gynecology and perineology: the balance of beauty and functionality.
What to do with urinary incontinence after childbirth?
Find answers to your questions and feel more confident.
What is important for every woman to know about the cervix?
Everything you need to know about the cervix is now collected in one article on the website of the "Daughter-mother".
Why should your mother visit a gynecologist?
We all understand why girls should visit a gynecologist. This specialist will help solve various problems related to women's health — from pregnancy management to the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. However, over time, when women get out of reproductive age, they begin to contact a gynecologist less and less often, mistakenly believing that they no longer need his help. But a gynecologist is not only about reproductive health, he can help in solving many other issues related to the female body. So what questions can your mother ask a gynecologist about?
How to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles?
Intimate problems are often hushed up, it is awkward to talk about them even with a doctor. However, if the issue concerns the health of the pelvic floor, it is better not to waste time and immediately consult a doctor. After all, problems with this area can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Uterine bleeding — is it worth sounding the alarm?
Abnormal uterine bleeding is when the bleeding goes beyond the normal menstrual cycle. The discharge may be more abundant or last longer. The "normal" menstrual cycle is different for everyone. But menstruation shouldn't be a problem for you.: a serious condition that prevents you from engaging in any activity, forces you to skip work or study. In the article we will tell you how to distinguish abnormal uterine bleeding.
Stress-free menopause: how hormone therapy helps women
With age, women experience a natural decrease in reproductive function, known as menopause. This process takes a long time and is accompanied by changes in the physical and emotional state, hormonal restructuring and complete cessation of menstruation. On average, menopause (the so-called last menstruation in a woman's life) occurs at the age of 45-55 years, but its precursors may appear earlier, and the process of "restructuring" the body can last for several years. A decrease in the level of female sex hormones leads to unpleasant symptoms that not only worsen the quality of life, but can also contribute to the development of serious diseases. Although menopause is not a disease and does not require treatment, there are methods to improve well-being and prevent complications. One of these methods is menopausal hormone therapy (MGT). The decision on the need and time of MGT is made by a gynecologist. To understand whether such therapy is necessary for all women, it is important to understand the nature and characteristics of menopause.
How to reach
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Zamoskvoretskaya line - exit 4 After exiting the subway, walk through the pedestrian tunnel and climb the stairs. Move towards the railway tracks, go down the stairs immediately after them and walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS.
Travel time
9 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Ring line - exit 2. After exiting the subway, turn left and walk to the pedestrian crossing. Cross the road through two pedestrian crossings and move along the Tverskoy overpass. Go down the stairs immediately after the railway tracks, walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS
Travel time
11 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign
From the metro station "Tsvetnoy Bulvar"
1 exit to the city, then left to the Garden Ring, at the crossing to the right, crossing the boulevard, one more crossing and at the traffic light to the left. The Olymp Clinic building is located overlooking the Garden Ring to the right of the crossing. Travel time is approximately 9 minutes. Landmark - sign Olymp Clini
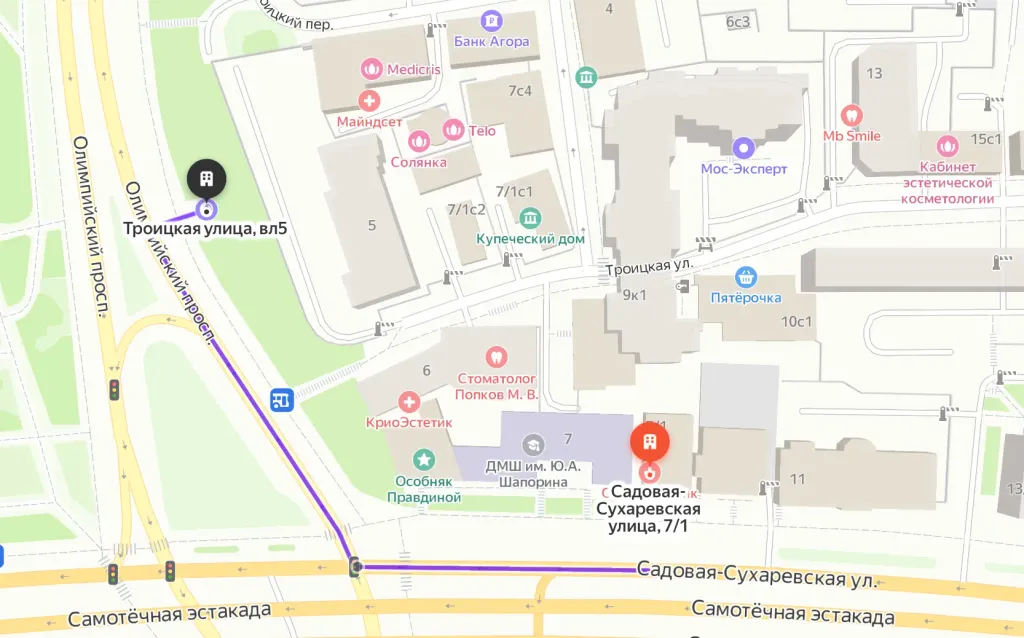
From the metro station "Sukharevskaya"
Exit 3 from the metro and 640 meters straight ahead, the clinic will be on the right. Landmark - sign Olymp Clinic
Parking lot map
Exit 3 from the metro and 640 meters straight ahead, the clinic will be on the right. Landmark - sign Olymp Clinic
From Sokol metro station
The last car from the center: follow the signs for Exit 5. From the glass doors to the right and go to the end of the passage. Exit to the city by the steps to the left. After exiting the crossing to the street, go straight along Leningradsky Prospekt to the intersection with Chapaevsky Lane. Next, turn right (onto Chapaevsky Lane) and walk to the Triumph Palace residential complex. Entrance to the territory: through checkpoint No. 1, opposite the Vkusville store, you will need to present your passport. After passing through the checkpoint, go up the stairs to the fountain, opposite it you will see our clinic.
Travel time
10-12 minutes
From the Airport metro station
The first car from the center: follow the Exit 2-3 signs. Turn left out of the glass doors and walk to the end of the passage. After exiting the crossing to the street, go straight along Leningradsky Prospekt to the intersection with Chapaevsky Lane. Next, turn left (onto Chapaevsky Lane) and walk to the Triumph Palace residential complex. Entrance to the territory: through checkpoint No. 1, opposite the Vkusville store, you will need to present your passport. After passing through the checkpoint, go up the stairs to the fountain, opposite it you will see our clinic.
Travel time
12-15 minutes
How to get
Entry to the territory is prohibited, but there are free city parking lots around the Triumph Palace residential complex, where you can easily find a place for your car. Free parking area:





