Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
Ultrasound allows you to visualize internal organs such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys and other structures.
Ультразвуковая диагностика дает возможность оценить состояние внутренних органов, выявить различные патологические состояния, включая хирургическую патологию (острый холецистит, острый аппендицит), изменения в структуре органов.
A high-frequency ultrasound machine is used for ultrasound. Modern sensors have high resolution and allow you to get a detailed image of small structures.
Benefits
Painlessness and safety
Ultrasound is a non—invasive and painless procedure that does not have a harmful effect on the body.
High information content
The study provides detailed information about the condition of internal organs, which helps in diagnosis.
Speed of implementation
The procedure takes a little time, the results are available immediately after the study.
A wide range of applications
Ultrasound is used to diagnose various diseases and control treatment, which makes it a universal research method.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
It is recommended to follow a few simple rules: 2-3 days before the study, exclude products that cause gas formation from the diet (legumes, cabbage, carbonated drinks), 6-8 hours before the procedure, refrain from eating and drinking, as well as not smoking or chewing gum.
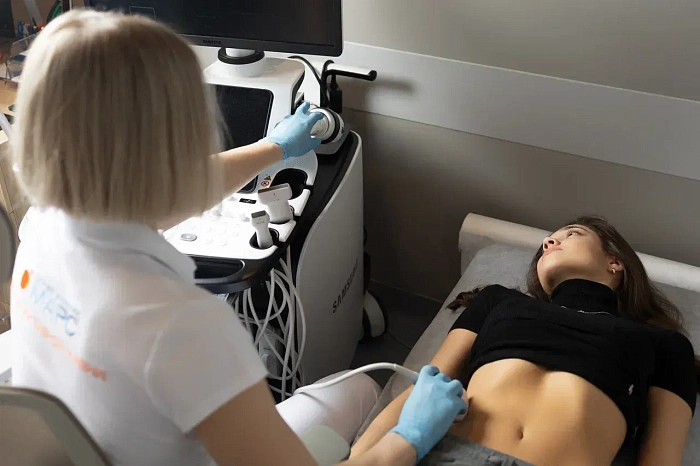
Abdominal ultrasound procedure
The doctor applies a gel to the patient's abdomen, which improves the contact of the sensor with the skin. Then the sensor of the ultrasound device moves along the surface of the abdomen, transmitting an image of the internal organs to the monitor. The doctor examines the abdominal organs, evaluates their size, structure and identifies possible pathologies. The procedure takes about 20-30 minutes.
Recommendations after ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
After an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, the patient can immediately return to normal business. It is important to follow the doctor's recommendations, especially if pathologies have been identified that require observation or treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I prepare for the procedure?
- Rye bread, pastries.
- Milk and dairy products.
- Legumes (peas, beans, lentils).
- Fresh vegetables and fruits (cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, apples, pears, grapes).
- Sweets, carbonated drinks.
Light dinner: Have a light dinner the night before and no later than 18:00-19:00.
Fasting: the study is conducted strictly on an empty stomach, so on the day of the study you can not eat or drink (water too) for 6-8 hours before the procedure.
Enterosorbents: if you have a tendency to gas formation, you can take an enterosorbent (for example, activated charcoal, espumizan) the day before the ultrasound.
Which organs are examined during ultrasound of the abdominal cavity?
Gallbladder: The shape, size, wall thickness, presence of stones, polyps, inflammation (cholecystitis) is assessed, and the patency of the bile ducts is assessed.
Pancreas: Size, structure, presence of neoplasms, inflammation (pancreatitis), cysts and other pathologies are assessed.
Spleen: Size, structure, presence of neoplasms, enlargement (splenomegaly), rupture and other pathologies are assessed.
Abdominal aorta and its branches: The diameter, the presence of aneurysm (expansion) or stenosis (narrowing), and blood clots are assessed.
Lymph nodes: Size, shape, structure, and the presence of inflammatory or tumor changes are assessed.
Abdominal cavity: The presence of free fluid (ascites) is assessed.
How long will it take for the results of the study to be ready?
In some cases, especially with complex studies or high doctor workload, the results may be ready in a few hours.
Less often, the ultrasound results may be ready the next day. This may be due to the need for more detailed image analysis or the workload of the clinic.
How often do I need to undergo the procedure for preventive purposes?
In the absence of complaints and risk factors, it can be performed less frequently – once every 3-5 years.
Didn't find an answer to your question?
You can describe your problem in detail and ask a question to the doctor. He will answer you and help you find a solution
Врачи
Смотреть всех врачейUltrasound diagnostician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Higher Qualifying Category Physician. Head of the Functional and Ultrasound Diagnostics department.
Ultrasound Diagnostics Doctor
Indications and contraindications
Indications
Abdominal pain of unclear etiology
The study helps to determine the cause of pain and identify possible pathologies.
Suspected liver and gallbladder diseases
Jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium and changes in blood tests.
Diagnosis of tumors and cysts
The study makes it possible to identify tumor formations and cysts in the abdominal organs.
Monitoring of the condition in chronic diseases
Regular ultrasound is necessary to monitor patients with chronic diseases of the liver, pancreas and kidneys.
Expected effect
Accurate diagnosis
Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of internal organs, which helps in making an accurate diagnosis.
Monitoring of chronic diseases
Monitoring the condition of patients with diseases of the abdominal cavity.
Identification of hidden pathologies
Detection of diseases in the early stages, when the symptoms have not yet appeared.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment
Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the results of the therapy and adjust the treatment.
Similar referral activities
Ultrasound of the joints
A diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of soft tissues, tendons, ligaments and cartilage structures of the joint. It is used to detect inflammatory, traumatic and degenerative changes in joints.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
A study that allows you to assess the condition and functionality of the gallbladder, as well as identify pathologies such as stones, inflammatory processes and neoplasms.
Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system
Ultrasound examination, which provides high-precision visualization of muscles, tendons, joints and bone surfaces, allows you to quickly identify injuries and diseases.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
A diagnostic method that allows you to evaluate the structure of breast tissue and identify pathological changes. Suitable for women of all ages and health conditions.
Ultrasound of soft tissues
A study that allows you to assess the condition of the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles, tendons, lymph nodes and blood vessels. It helps to identify inflammatory processes, hematomas, tumor formations and traumatic injuries.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Ultrasound allows you to visualize and assess the condition of the internal organs of the pelvis in women and men. In women, the study includes examination of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, in men — the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.

