Intervertebral hernia
Pathological protrusion of a part of the intervertebral disc beyond its anatomical boundaries.

Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers, reducing the load on the spine during movement. They consist of a fibrous ring and a pulpous nucleus, which provides flexibility and elasticity of the spinal column. With age or under the influence of adverse factors, discs lose moisture, become thinner and less durable. The formation of a hernia begins with the degeneration of the intervertebral disc, when its tissues are destroyed and lose their ability to withstand the load. Over time, microcracks appear in the fibrous ring, through which the nucleus pulposus can partially extend beyond the disc. Depending on the degree of damage, protrusion (initial stage) and a full-fledged hernia are distinguished.
Causes
Degenerative processes in the spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis)
Regular static loads
Weight lifting, sudden movements, and dynamic overloads
Spinal injuries
Curvature of the spine
Excess body weight
Congenital anomalies of the spinal column
Symptoms
Back pain that increases with movement, bending, and exertion
Feeling of stiffness and tension in the back muscles
Radiating pain to the arm or leg
Sensitivity disorder
Decreased strength in limbs, weakness, paresis
After-effects
The most dangerous complication is myelopathy, which develops when the spinal cord is compressed. The condition is accompanied by increasing muscle weakness, impaired sensitivity, and pelvic organ dysfunction. In our clinic, you can perform an MRI scan, as well as undergo a study of evoked potentials that will help identify pathology and avoid complications.
Лечение
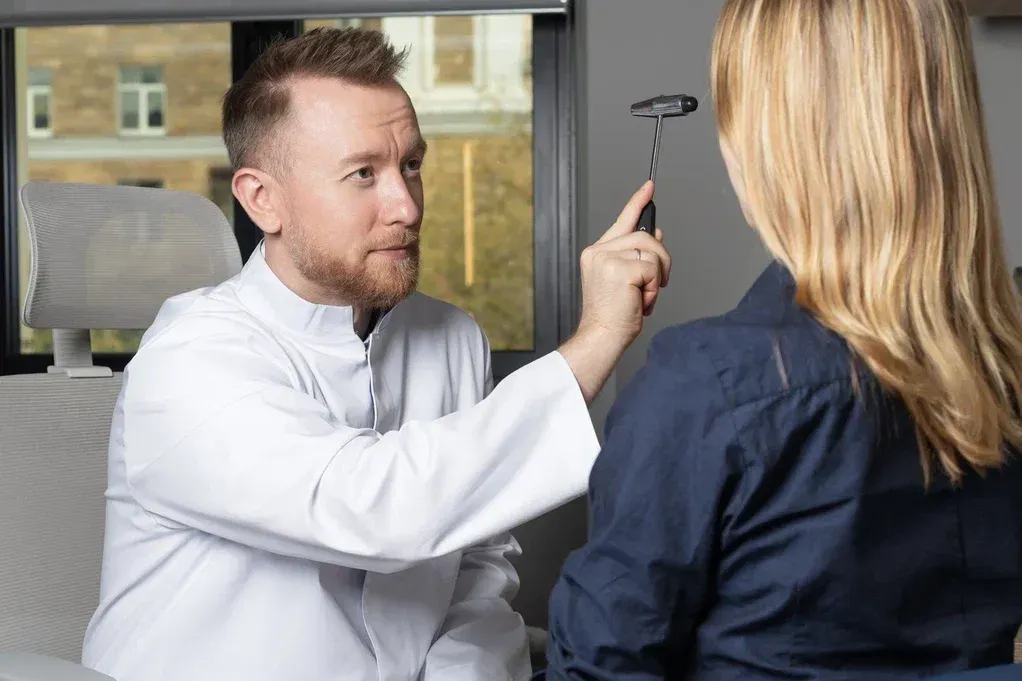
Conservative treatment
First of all, drugs are used that reduce inflammation and pain. Physiotherapy methods help to accelerate tissue repair. Physical therapy (physical therapy) plays an important role, aimed at strengthening the muscular corset and improving the mobility of the spine. The set of exercises is selected individually.

Surgical treatment
The operation is performed in cases where conservative therapy has no effect. The most common methods are: — Microdiscectomy — removal of hernial protrusion through a small incision. — Endoscopic discectomy is a minimally invasive operation that is performed through small punctures using an endoscope. — Laminectomy — removal of a part of a vertebra for decompression of nervous structures. — Laser vaporization is the evaporation of a part of the nucleus pulposus using a laser. After surgery, the patient needs a rehabilitation course, including therapeutic gymnastics, physiotherapy and a gradual return to physical activity.
Schedule a visit to the clinic
How to reach
Moscow, 1st Yamskogo Polya Street, 15
Mon–Sun Around the clock
+7 495 255-50-03
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Zamoskvoretskaya line - exit 4 After exiting the subway, walk through the pedestrian tunnel and climb the stairs. Move towards the railway tracks, go down the stairs immediately after them and walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS.
Travel time
9 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Ring line - exit 2. After exiting the subway, turn left and walk to the pedestrian crossing. Cross the road through two pedestrian crossings and move along the Tverskoy overpass. Go down the stairs immediately after the railway tracks, walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS
Travel time
11 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign


