Ovarian cyst
A benign formation in the form of a cavity filled with fluid that forms on the surface or inside the ovary.

Ovarian cysts often occur as part of a normal menstrual cycle. For example, follicular cysts form when the follicle containing the egg does not rupture during ovulation. Luteal cysts appear after ovulation if the follicle fills with fluid after the egg is released. However, there are also pathological cysts, such as dermoid (containing hair, teeth, and skin tissues), endometrioid (associated with endometriosis), and cystadenomas (benign or malignant tumors). These cysts can cause symptoms and require medical intervention. To prevent ovarian cysts, it is important to visit a gynecologist regularly (at least once a year), as well as monitor hormonal balance, especially in the presence of PCOS or endometriosis. If symptoms appear (pain, cycle disturbance), consult a doctor immediately.
Causes
Physiological processes: follicular and luteal cysts are associated with the menstrual cycle
Hormonal disorders: estrogen and progesterone imbalance, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Endometriosis: the spread of endometrial cells outside the uterus
Genetic predisposition
Infections and inflammations of the pelvic organs
Taking hormonal medications or ovulation stimulants
Ovarian injuries
Symptoms
Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen that increases before menstruation
Menstrual irregularity (irregular or painful periods)
Intermenstrual spotting
Pain during sexual intercourse
Frequent urination or feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
Feeling of heaviness or fullness in the stomach
Increased abdominal volume
Nausea, vomiting (if the cyst is twisted or ruptured)
After-effects
Most ovarian cysts are not dangerous and resolve on their own. However, some can lead to complications. Cyst torsion is accompanied by acute pain and requires emergency surgery. Cyst rupture can cause internal bleeding and peritonitis. Large cysts or multiple formations (for example, in PCOS) can interfere with ovulation. In rare cases, cysts can degenerate into malignant tumors.
Лечение
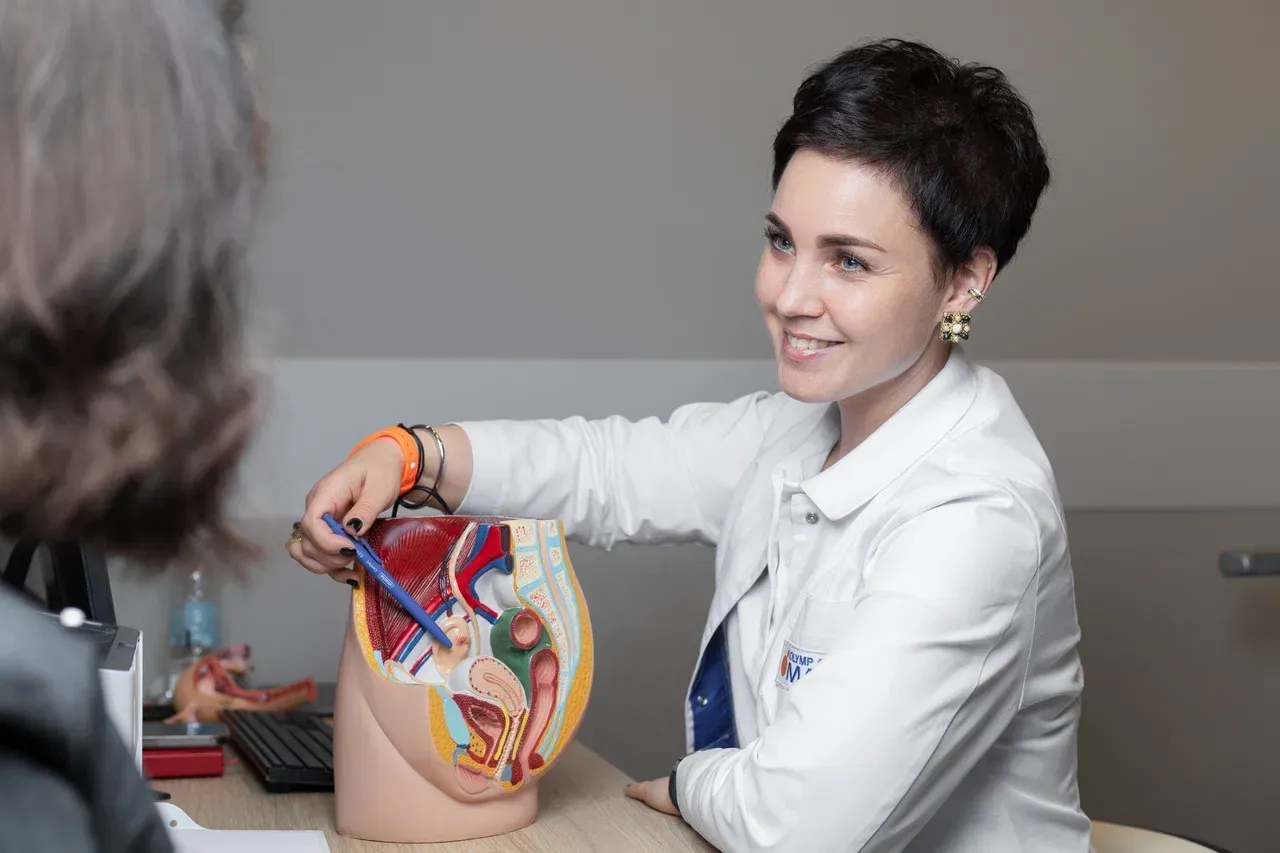
Conservative treatment
If the cyst is small and does not cause symptoms, the doctor may recommend follow-up. Functional cysts often disappear on their own after 1-2 menstrual cycles. Regular ultrasounds are performed to monitor the condition. Hormonal medications such as oral contraceptives are prescribed for hormonal disorders or endometriosis, which help reduce the size of cysts and prevent the formation of new ones. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain.
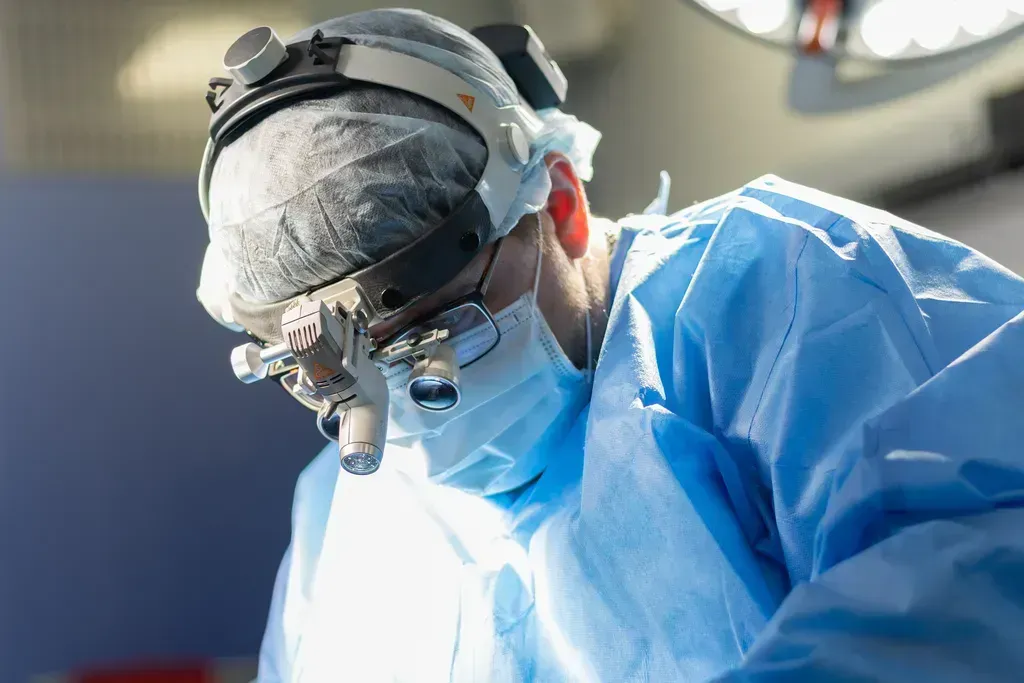
Surgical treatment
Surgery is required for complications (torsion, rupture) or suspected malignancy. The main method is laparoscopic cystectomy, a minimally invasive operation in which the cyst is removed through small incisions. In more complex cases, for example, with large cysts or suspected cancer, laparotomy, an open operation, may be required. If the cyst has caused significant damage to the ovarian tissue, an oophorectomy is performed — removal of the ovary.
Schedule a visit to the clinic
How to reach
Moscow, 1st Yamskogo Polya Street, 15
Mon–Sun Around the clock
+7 495 255-50-03
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Zamoskvoretskaya line - exit 4 After exiting the subway, walk through the pedestrian tunnel and climb the stairs. Move towards the railway tracks, go down the stairs immediately after them and walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS.
Travel time
9 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign
How to get
From the Belorusskaya metro station of the Ring line - exit 2. After exiting the subway, turn left and walk to the pedestrian crossing. Cross the road through two pedestrian crossings and move along the Tverskoy overpass. Go down the stairs immediately after the railway tracks, walk along the house, then turn right onto 1st Yamskoye Pole Street. At the turn to 3rd Yamsky Pole Street, cross the road at the pedestrian crossing and continue along 1st Yamsky Field Street, after a few buildings on the left you will see Olympus Clinic MARS
Travel time
11 minutes
Landmark
Olympus Clinic MARS sign


